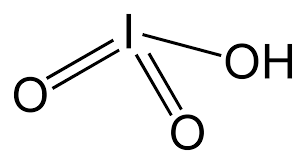
Iodic Acid
100 INR
Product Details:
- CAS No 7782-68-5
- Grade ACS reagent
- Type Scientific Lab Chemicals
- Purity(%) 99.5% (RT)
- Click to View more
X
Iodic Acid Price And Quantity
- 100 INR
- 1 Piece
Iodic Acid Product Specifications
- ACS reagent
- 7782-68-5
- 99.5% (RT)
- Scientific Lab Chemicals
Iodic Acid Trade Information
- MUMBAI
- Cash in Advance (CID) Cash Advance (CA)
- 10 Piece Per Week
- 3-4 Week
- Australia Eastern Europe Central America Africa Middle East South America Western Europe Asia North America
- All India
- ISO CERTIFICATE : 9001:2015
Product Description
Iodic acid
puriss. p.a., ACS reagent, 99.5% (RT)
Description
General description
Iodic acid is the hydrated form of I2O5.Reaction of iodic acid with hydrogen iodide has been described by electrolytic dissociation theory. Combustion of mixture of chromic, iodic, sulfuric and phosphoric acids has been proposed. Its Raman spectra have been recorded. Vibrational assignment of IO3- has been evaluated.
Other Notes
Oxidant for the decomposition of metals and organic compounds
| grade | ACS reagent |
| | |
| grade | puriss. p.a. |
| assay | 99.5% (RT) |
| impurities | 0.1% total nitrogen (N) |
| ign. residue | 0.01% (as SO4) |
| anion traces | bromide, chloride (as Cl-): 200 mg/kg |
| iodide (I-): 5 mg/kg | |
| sulfate (SO42-): 150 mg/kg | |
| cation traces | Ag: 5 mg/kg |
| Al: 5 mg/kg | |
| Ba: 10 mg/kg | |
| Bi: 5 mg/kg | |
| Ca: 10 mg/kg | |
| Cd: 5 mg/kg | |
| Co: 5 mg/kg | |
| Cr: 5 mg/kg | |
| Cu: 5 mg/kg | |
| Fe: 10 mg/kg | |
| K: 50 mg/kg | |
| Li: 5 mg/kg | |
| Mg: 5 mg/kg | |
| Mn: 5 mg/kg | |
| Mo: 5 mg/kg | |
| Na: 50 mg/kg | |
| Ni: 5 mg/kg | |
| Pb: 5 mg/kg | |
| Sr: 5 mg/kg | |
| Tl: 5 mg/kg | |
| Zn: 5 mg/kg |
-
CAS Number
7782-68-5
-
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation) HIO3
-
Molecular Weight 175.91
Enter Buying Requirement Details






 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Send SMS
Send SMS Call Me Free
Call Me Free